Cryptocurrency Arbitrage: Everything You Need to Know in One Article
The cryptocurrency market is active and diverse, so it offers users numerous tools for earning. Arbitrage can be considered one of the least risky and easy to understand, which attracts the attention of traders of various levels, and especially beginners. Due to the clear work process and low entry threshold, the use of this type of trading has become widespread, although it has been somewhat transformed over the years of its existence.
In this article, the editors of Incrypted will analyze what cryptocurrency arbitrage is, how to use it in practice, and whether it is really possible to make a profit.
What is cryptocurrency arbitrage in simple words
Cryptocurrency arbitrage refers to the purchase of a digital asset with the aim of instantly selling it at a higher price than when buying it on another market or in another trading pair. For example, a trader can buy 1 SOL on exchange X for 130 USDT and then immediately sell it on exchange Y for 140 USDT. The difference of 10 USDT is the arbitrator’s earnings.
Market opportunities for traders in this case create price gaps (gaps) that are formed between different trading platforms or pairs due to the balance of supply and demand. This is due to the fact that each trading pair, and even more so the exchange, is, in fact, a separate market with its own pricing. And although today’s gaps are not as significant as they were in the early stages of the industry, they can still generate some income.
Both ordinary traders and market makers, as well as developers of software that allows you to track the difference in quotations and automatically execute relevant deals, can potentially earn from this type of trading.
Among other types of trading, arbitrage stands out:
- low risk . Theoretically, you can get income risk-free, because buying and selling takes place before the price has time to change significantly. However, in certain cases, for example, during a transfer from exchange to exchange or execution of an order, price fluctuations are still possible, which should be taken into account when forming a strategy;
- speed Since quotes on the crypto market change very quickly, arbitrageurs have to make deals in a matter of minutes or even seconds. Therefore, specialized software in the form of arbitrage trading bots or scanners is often used for such operations;
- large volumes of transactions . As a rule, the net profit relative to the funds invested in arbitration is quite small (rarely exceeds 5-10%), therefore, in order to obtain tangible income, it is necessary to conduct transactions with large sums.
From the perspective of the markets, arbitrage is a trading activity that helps minimize price gaps and maintain a stable value of an asset across all platforms where it is traded. Stable prices on modern CEX would be impossible without professional large arbitrageurs, as well as specialized programs and algorithms.
How arbitration appeared
The French word “arbitrage” (court decision) in the context of economics and finance was first used in 1704 by the French mathematician Mathieu de la Porte in his treatise “La science des négociants et teneurs de livres”. In his work, the scientist analyzed exchange rates in order to identify the most profitable places for receiving and paying money by promissory note.
The history of cryptocurrency arbitrage began with the emergence of the digital asset market, which at the initial stages of existence was characterized by low liquidity, few trading platforms and distributed, relatively small capital. The difference in the value of bitcoin on individual exchanges at that time could be several tens of percent due to the absence of large market makers and the peculiarities of pricing in different jurisdictions.
For example, there was a large price gap in African markets in 2017 – at one point the price of BTC on the Golix platform was 87% higher than the average on other centralized exchanges (CEX). And in January 2018, former CEO of FTX and co-founder of Alameda Research, Sam Bankman-Fried, organized arbitrage trading, profiting from a 10% price gap between Bitcoin in the US and Japanese markets.
It is also worth mentioning the so-called “Kimchi premium” – a price premium that has been observed for many digital assets on Korean crypto exchanges since 2016. The reason is the same as in the case of Japan – strict regulations and limited access for foreigners to trade. By the way, in March 2024, the largest “Kimchi premium” for Bitcoin in the amount of 10% was recorded in 27 months.
Before the emergence of big capital in the crypto industry, arbitrage opportunities were widely available to ordinary traders. However, since 2017, almost all the profitable lines on centralized exchanges (CEX) have passed into the hands of whales and market makers, who can react to breaks faster due to automation and have more opportunities to make international deals.
A similar situation occurred in decentralized finance (DeFi) — at an early stage of development, ordinary users also had the opportunity to earn on cryptocurrency arbitrage, trading between centralized and decentralized exchanges (DEX) or various liquidity pools. Currently, the lion’s share of arbitrage agreements falls on bots that can track transactions even before they are included in the blockchain.
What is P2P arbitration and how does it work?
P2P (peer-to-peer) arbitrage is a type of arbitrage agreement that involves buying and selling assets directly between market participants. The main feature of P2P trading is the contractual price, which may differ from the market price, which opens up opportunities for profit.
For example, a user can buy bitcoin directly on the exchange and sell it more profitably on a P2P platform by responding to another user’s ad. A more complex version of P2P arbitrage involves the independent opening of bids for purchase or sale — in this case, the trader himself sets the price of the offer, which may differ from the market one in one way or another.
It is important to understand what exactly causes the price gap. In the case of P2P, users are willing to sell lower or buy higher if they receive some benefit, such as a transaction without verification, direct withdrawal without fees, or exchange for a rare fiat currency. Therefore, before starting work, it is worth studying several P2P sites, their advantages for users and pricing mechanisms.
Arbitration relations: structure and algorithm of actions
Arbitrage bonds are a central concept in cryptocurrency arbitrage. Basically, these are algorithms that describe the necessary actions in order to make money from price differences. The simplest arbitration bond looks like this:
- Buy bitcoin at price X on platform A.
- Transfer it to the B exchange.
- Sell on exchange B at price Y, which must be higher than price X.
However, the connections are usually more complex and may involve intermediate steps, involve the use of multiple fiat currencies, or the transfer of funds between centralized and decentralized platforms.
The execution of all actions is called a circle. The profitability of the connection is estimated as a percentage of the invested capital, which was earned after passing one round. For example, a return of 10% means that an arbitrageur can earn 10% of his deposit in one round.
Top 3 types of cryptocurrency arbitrage
There are three main types of digital asset arbitrage — international, inter-exchange and intra-exchange.
International arbitrage trading requires the use of trading platforms in several countries, as well as access to local payment methods and fiat currencies, which significantly complicates the use of this method of earning by beginners.
The essence of inter-exchange arbitrage is to purchase cryptocurrency on one platform and then sell it on another. This method requires multiple accounts, and when using it, you should take into account transaction costs, such as transfer fees, and possible time delay due to network congestion or other factors.
Intra-exchange arbitrage involves trading on the same platform, but between different trading pairs. For example, you can buy Bitcoin for $50,000, then exchange it for 20 ETH on the same service, and then sell 20 ETH for 52,000 USDT, taking advantage of the price gap between the different pairs. The main advantage of this method is speed and the absence of transfer fees between exchanges.
Separately, it is worth highlighting DEX-arbitrage, the mechanism of which is significantly different and is based on liquidity pools, slippage, the value of the asset in different networks and even the sequence of transactions in the mempool.
Another, less common tool in this market is spot-futures arbitrage, the essence of which is to make money on the difference between the prices of cryptocurrency futures contracts and the value of related assets.
Scanners. What to use?
Exchange order books and blockchain transactions are publicly available, and most cryptocurrency exchanges provide an application programming interface (API) with access to up-to-date price data. This means that information about the value of a digital asset in different markets can be aggregated and analyzed to identify arbitrage opportunities. Here are some tools traders use to find market opportunities:
- data aggregators . An example is Cryptorank Arbitrage , or CoinMarketCap , which offers a complete list of markets for each cryptocurrency, which allows you to monitor the exchange rate difference in different trading pairs and on different crypto exchanges. To track DEX prices, you can use services like DexScreener ;
- scanner bots , which in semi-automatic or automatic mode track the current prices of digital assets on various platforms and, in case of detecting a sufficient price gap, notify the user about it. Typically, such applications use exchange APIs and ideally should take into account the availability of the crypto pair on both markets, market liquidity, transfer fees and network load. Another advantage is that the scanners can be adapted for different types of arbitration;
- arbitrage trading bots that automatically scan asset prices and, if a gap is detected, independently execute a trade deal via API. Such solutions can be paid or free – the specific cost and set of functions depends on the provider.
In addition to open data aggregators and specialized software, arbitrators, especially beginners, use other sources of information to search for profitable deals:
- Telegram channels with different connections and signals. It should be taken into account that they usually offer information late or try to simply sell their product to the audience;
- various closed communities (such as private chats) that can offer more up-to-date information than public sources, but are associated with the same risks and, in addition, require additional costs;
- some social media influencers like X (formerly Twitter) frequently post information related to arbitration and communications.
The reliability and relevance of such data depends on the source. As a rule, access to really working connections is limited and no one can predict how long the direction will be profitable. Therefore, it is important to learn to independently analyze the market in search of opportunities.
How to start cryptocurrency arbitrage: a step-by-step guide
To earn income on price gaps, first of all, you need to decide on the type of arbitrage that will be used and form your strategy taking into account the limitations and features of specific platforms.
However, the basic algorithm of actions is almost the same in all cases. Here, for example, is a step-by-step instruction for the most understandable and simple – inter-exchange – arbitration:
- Choose several reliable cryptocurrency exchanges and create accounts on them. Verify and meet other requirements to access trading features.
- Deposit to all registered accounts. If you already know the direction of the deal, you can adjust the capital allocation accordingly.
- Using the above analysis tools, find the difference in quotes of a particular trading pair on different exchanges.
- If you find it, buy an asset on the exchange with a lower price (for this, place a purchase order), and then, as soon as possible, transfer it to another platform and sell it.
By following these simple steps, a trader can start using cryptocurrency arbitrage for potential profits. However, it is always worth considering the risks, as well as the operational costs associated with such deals.
Is arbitration legal?
Arbitrage is a legal trading activity subject to compliance with regulatory requirements on the platforms used. These rules may include identity verification, compliance with trading limits, and verification of payment means.
The main charge an arbitrator can face is money laundering. However, to avoid it, it is enough to prove the origin of the deposited assets. You should also not use mixers or other anonymization tools, as the transactions associated with them are often considered high-risk and may be blocked.
When using specialized software that involves direct connection to an exchange account (automated API trading), it is worth studying the policy of the exchange regarding the possibility of applying such solutions. In addition, do not forget that such services get access to your assets.
It is worth noting that the problem of the legality of transactions becomes more complicated with an increase in the number of jurisdictions and points of interaction with fiat currencies. So, for example, in not all countries, banks support transfers to crypto exchange accounts or withdrawal of funds from them, and some local platforms may be closed to foreigners. Therefore, for example, international arbitration requires painstaking and detailed study of all steps and aspects of conducting transactions.
On which exchanges to register for arbitration
The specific list of platforms depends on the volume of your transactions and the type of exchange (CEX or DEX). As a rule, the largest price gap is formed between pairs on top exchanges and little-known platforms, so accounts on such centralized platforms as Binance, Kraken, ByBit and others may be needed.
In order to determine the list of priority services, it is first necessary to investigate the possible areas of arbitration. For example, you can use the Cryptorank Arbitrage service , which immediately displays possible directions of transactions.
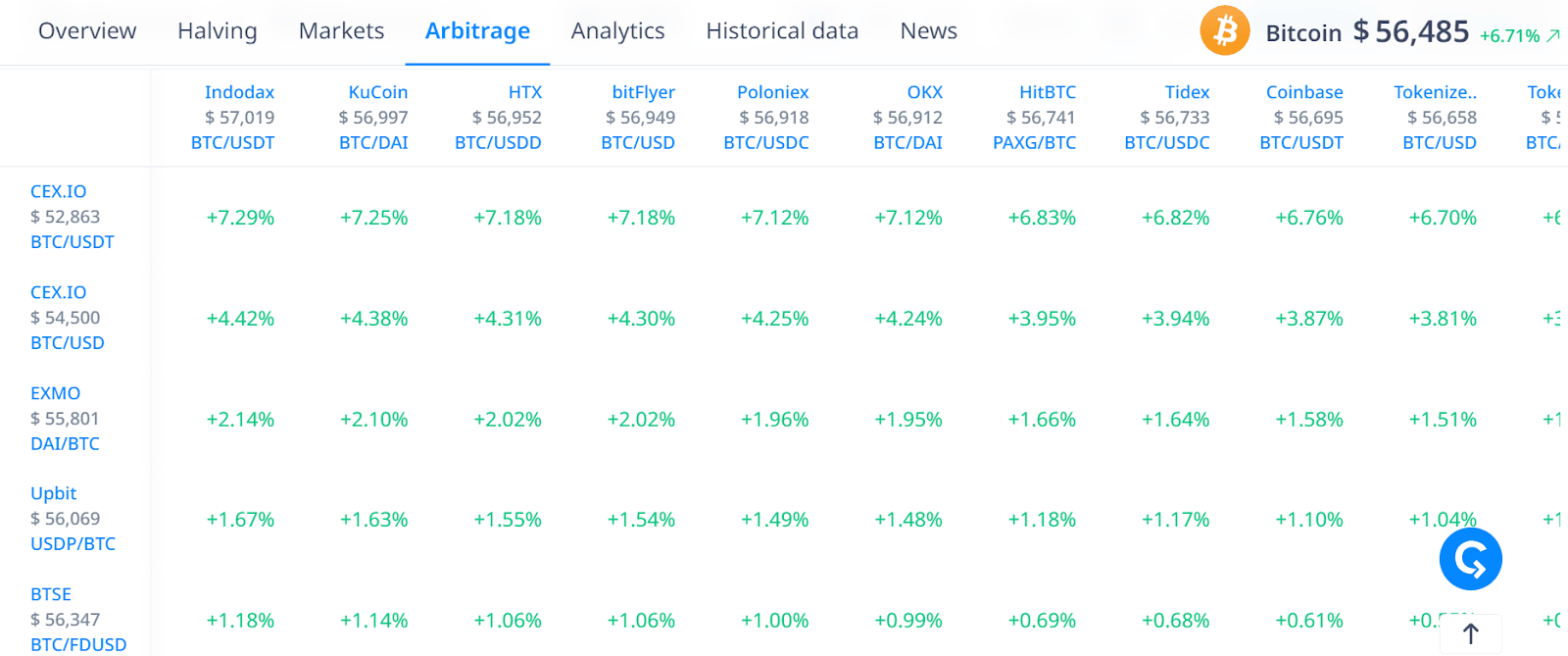
In addition, solutions for the automation of cryptocurrency arbitrage, as a rule, support a limited range of CEX and DEX, the list of which is published on the official website of the product or in the description of the service. Therefore, it is worth proceeding to account registration only after a detailed study of the software.
A general rule of thumb for a professional arbitrageur is that the more accounts, the more potential opportunities. However, registration and verification on the exchange, as well as deposit and withdrawal of funds, are not always smooth, especially when it comes to closed local platforms or completely unknown exchanges. It is important to maintain a balance between the number of accounts, the complexity of their maintenance and the efficiency of use.
Conclusion
Cryptocurrency arbitrage is one of the least risky types of trading that attracts beginners due to its clarity and low entry threshold. It also brings certain benefits to the crypto market, as it allows to reduce the fragmentation of capital and ensure a stable value of the asset, regardless of the platform or trading pair.
In the early stages of the market’s existence, arbitrage was available to ordinary users and provided opportunities for earning even with a small capital. Currently, this niche is mainly occupied by professional market makers, whales and specialized trading bots. However, traders can still earn income from arbitrage trading using special tools and the results of their own research.
